 Organized at #AHAIC2021 (an African-led biennial global health convening hosted by Amref Health Africa) by International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers and Associations (IFPMA), the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), the Global Innovation Policy Center (GIPC), and The Innovation Council was held on 8 March 2021.
Organized at #AHAIC2021 (an African-led biennial global health convening hosted by Amref Health Africa) by International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers and Associations (IFPMA), the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), the Global Innovation Policy Center (GIPC), and The Innovation Council was held on 8 March 2021.Bringing you the Lastest Updates about Health Innovations and Technologies
Media corner and Publications
Leveraging Innovation Technologies to Respond to Malaria, a Systematized Literature Review of Emerging Technologies09, February 2023
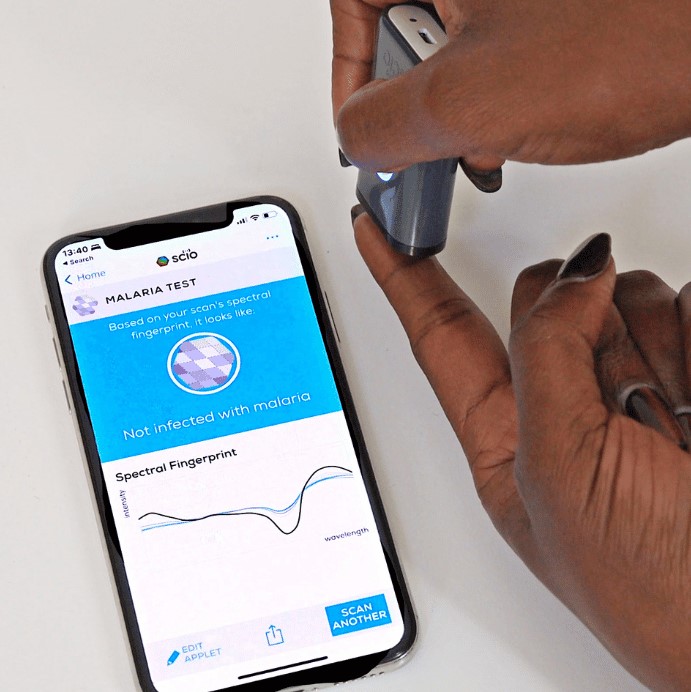 Malaria remains one of the leading causes of death among children under five in sub-Saharan Africa, accounting for 80% of all deaths. However, with accelerated pace of technological innovations in the world, this presents an opportunity to harness innovative interventions to step up the fight against the scourge of malaria. The current malaria response efforts are faced with a myriad of systemic constraints ranging from the provision of accessible and accurate diagnostic tests, effective surveillance and monitoring systems, and availability of countermeasures to reduce transmission levels.
Malaria remains one of the leading causes of death among children under five in sub-Saharan Africa, accounting for 80% of all deaths. However, with accelerated pace of technological innovations in the world, this presents an opportunity to harness innovative interventions to step up the fight against the scourge of malaria. The current malaria response efforts are faced with a myriad of systemic constraints ranging from the provision of accessible and accurate diagnostic tests, effective surveillance and monitoring systems, and availability of countermeasures to reduce transmission levels.
Deployment of innovative technologies have significantly contributed to the prevention and control of malaria in other parts of the world. So, to make these innovative tools available and accessible to countries in Africa, WHO conducted a systematized review to identify key technological innovations targeting different areas of the malaria response, which include surveillance, microplanning, prevention, diagnosis and management. This was in response to the existing knowledge gap about the comprehensive technological landscape for malaria response.
The study also highlighted key drivers including infrastructural requirements to foster development and scaling up of innovations. In order to stimulate development of such innovations in Africa, countries should prioritize investment in infrastructural development, policy alignment and incentive frameworks for the localisation and integration of emerging technologies to create a more resilient and informed health infrastructure in Africa.
Find the article here
WHO AFRO: Towards a Healthcare Innovation Scaling Framework09, December 2022

WHO AFRO: Towards a Healthcare Innovation Scaling Framework
Cultivating supportive innovation ecosystems is key to the integration and sustainable scaling of healthcare innovations.
The World Health Organization in Africa conducted a 2-year follow up study of 2415 innovators who participated in the inaugural WHO AFRO innovation challenge in 2018, with the view to understand key drivers and challenges that contributed to either successes or failures to scaling up their respective innovations. The study led to the formulation of an evidence-based healthcare innovation scaling framework comprising 10 pillars with proposed indicators. The insights gained from the study are critical for national governments and other key stakeholders in assessing the capacity of local innovation ecosystems to support sustainable scaling up of innovations. In addition, the framework provides evidence on areas of investment and support towards building a robust ecosystem that harnesses innovations responding to local innovation needs.
Direct link to article: https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/23/15515
Towards a Healthcare Innovation Scaling Framework - The Voice of the Innovator.pdf ( 948.04 KB )
Harnessing technological innovations for COVID-19 Vaccine Delivery21, May 2021
 Innovations for vaccine delivery present exciting opportunities to enhance the impact and cost-effectiveness of almost every vaccination program, including the current roll out of COVID-19 vaccines. However, countries are not always in the know of the existing vaccine delivery innovations that could potentially be implemented in their context. Many of these innovations have been developed and deployed in other parts of the world. Therefore, at this moment where the efficient and effective rolling out of COVID-19 vaccines is advocated for, it is crucial to profile existing successful vaccine delivery technologies to facilitate horizontal scaling and adoption especially to the benefit of the African region.
Innovations for vaccine delivery present exciting opportunities to enhance the impact and cost-effectiveness of almost every vaccination program, including the current roll out of COVID-19 vaccines. However, countries are not always in the know of the existing vaccine delivery innovations that could potentially be implemented in their context. Many of these innovations have been developed and deployed in other parts of the world. Therefore, at this moment where the efficient and effective rolling out of COVID-19 vaccines is advocated for, it is crucial to profile existing successful vaccine delivery technologies to facilitate horizontal scaling and adoption especially to the benefit of the African region.
In an effort to make innovations accessible and available to countries in Africa, this paper presents a review and analysis of one thousand key technological innovations that have been developed from different parts of the world targeting different areas of vaccine delivery intervention areas. The study was undertaken with the view to provide African countries and other key stakeholders with information relating to technologies that can be adapted in their different contexts as they strengthen their vaccine delivery strategies.
017_WHO-AFRO_Vaccine-Delivery-Innovations_A4.pdf ( 420.76 KB )
Press briefing on possible #COVID19 resurgence & vaccine rollout in Africa06, May 2021
Watch the recorded session of the press briefing on possible #COVID19 resurgence & vaccine rollout in Africa with @WHOAFRO's Dr @MoetiTshidi & @Gavi's @MaphosaThabani
Women in Innovation: Providing leadership, creating solutions and driving change28, March 2021
Podcast on innovation in COVID-1916, February 2021
COVID-19 has spurred innovations across Africa. Listen to how WHO Afro and partners are supporting innovations across the continent.
Plenary: Innovation for Health - CCGH14, February 2021
 Every year, the Canadian Conference on Global Health (CCGH) brings together inspiring speakers to motivate, advocate, and share knowledge around critical topics in global health.
Every year, the Canadian Conference on Global Health (CCGH) brings together inspiring speakers to motivate, advocate, and share knowledge around critical topics in global health.
Click to watch the Recorded Session for CCGH 2020.
Scaling up Health Innovations in Africa08, January 2021
 This study on the 2018 WHO Africa Innovation Challenge has highlighted some of the successes and challenges surrounding the scaling of health innovations in the African Region today.
This study on the 2018 WHO Africa Innovation Challenge has highlighted some of the successes and challenges surrounding the scaling of health innovations in the African Region today.
The Innovation Challenge demonstrated the capacity for the African innovators to create innovative homegrown solutions that meet pressing health demands in their own communities. Many have been able to scale and have demonstrable impacts on their health systems and develop business models that are selfsustaining. However, these innovators continue to face challenges.These challenges will require a cross sectoral approach involving government, private sector actors, regulators, funders, educational institutions, research bodies and development partners from the health, education, technology, financing, infrastructure, and other domains. To inform these efforts and interventions, WHO Africa has undertaken a two-year follow up study on the best profiled innovators from the Innovation Challenge. This study aims to examine the experiences of African innovators in their innovation journey with the view to inform innovation ecosystem players that include governments, private sector, innovators, and other partners, to make informed decisions on what has worked, what strategies can be used to successfully scale highpotential health innovations in the Region, and what challenges remain.
This paper presents an overview of the initial observations from the 2018 WHO Africa Innovation Challenge and the subsequent analysis, observations and recommendations drawn from the experiences and insights of the innovators from the winning cohort upon follow up for two years.
011_WHO-AFRO_Scaling-Health-Innovations-in-Africa_A4_V1.pdf ( 1.36 MB )
COVID-19 could be springboard for African innovations28, December 2020
 The COVID-19 pandemic could be a blessing in disguise for Africa’s future growth because innovative ideas for addressing it could chart a path for future tech-based economies, scientists say. The technologies that have been developed in response to COVID-19 in Africa include WhatsApp Chatbots in South Africa, self-diagnostic tools in Angola, contact tracing apps in Ghana and mobile health information tools in Nigeria.
The COVID-19 pandemic could be a blessing in disguise for Africa’s future growth because innovative ideas for addressing it could chart a path for future tech-based economies, scientists say. The technologies that have been developed in response to COVID-19 in Africa include WhatsApp Chatbots in South Africa, self-diagnostic tools in Angola, contact tracing apps in Ghana and mobile health information tools in Nigeria.
“Africa’s future is dependent on technology and innovation, which are crucial for addressing the challenges of low structural transformation and inclusive development on the continent,” says Moredreck Chibi, WHO Africa regional advisor for innovation, in an interview with SciDev.Net this month. “There is a need for investing in innovation as an absolute and fundamental shift in the continent’s traditional business model.”
COVID-19 African Innovation Compendium03, December 2020
 The COVID-19 has increased demand for innovations that stem from the extreme need to find immediate and sustainable solutions to response to the pandemic. These innovative solutions are required at every level of the health systemspolicy, governance, service delivery, diagnostics and treatment, etc.
The COVID-19 has increased demand for innovations that stem from the extreme need to find immediate and sustainable solutions to response to the pandemic. These innovative solutions are required at every level of the health systemspolicy, governance, service delivery, diagnostics and treatment, etc.
It is however encouraging to note that since that COVID-19 sets its foot on the African continent, countries developed and deployed innovative home grown approaches as part of their COVID-19 response strategies. Therefore, this compendium seeks to highlight a selection of the home grown innovations that emerged from Africa in addressing the challenges of COVID-19. Many of these innovations can be scaled effectively within the region or repurposed in a post-COVID-19 context to further advance health and development goals.
This compendium reinforces the need for a comprehensive regional strategy for scaling health innovations by underscoring the importance of innovation as a transformative approach to accelerating progress towards the achievement of both
UHC and the SDGs.
WHO-AFRO_COVID-19_African-Innovation-Compendium.pdf ( 6.53 MB )
Global Landscape for Technological Innovations for COVID-19:Lessons for Africa03, December 2020
 This paper presents an analysis of a compilation of key technological innovations that have been developed across the world currently being used to address COVID-19 pandemic targeting various areas of the response as adopted from the WHO COVID-19 response strategy.
This paper presents an analysis of a compilation of key technological innovations that have been developed across the world currently being used to address COVID-19 pandemic targeting various areas of the response as adopted from the WHO COVID-19 response strategy.
The study was undertaken to bring to the surface potential impactful and contextually relevant innovations that can be adapted in Africa. This was in response to the existing knowledge gap about the technological landscape as it relates to COVID-19. The platform provided the much-needed information for countries including other key stakeholders to make informed decisions in adopting some of these technologies as part of the COVID-19 response in their respective countries. It is envisaged that countries and local innovators can approach the Intellectual Property owners of the profiled innovations for further collaboration in bringing these technologies to the African market.
STRATEGY FOR SCALING UP HEALTH INNOVATIONS IN THE WHO AFRICAN REGION02, December 2020
.png) With the increasing rate of globalization, innovation has become a key differentiating transformative feature that defines the long-term sustainable impact on improving the quality of life of the world’s population. There is an even greater demand for Africa to intensify its innovation effort to address its contextual challenges.
With the increasing rate of globalization, innovation has become a key differentiating transformative feature that defines the long-term sustainable impact on improving the quality of life of the world’s population. There is an even greater demand for Africa to intensify its innovation effort to address its contextual challenges.
The demand for innovation is even higher in the health sector where health outcomes are poor, despite global progress in reducing deaths among mothers and children and fighting infectious diseases. Worse health outcomes are experienced in fragile contexts and among marginalized groups. This strategy presents an opportunity for the Member States to strengthen their innovation systems to make them responsive to the innovation needs of the African Region. Success in developing a functional innovation system that harnesses and scales up new and improved innovations will be a key determinant in achieving UHC and the health-related SDGs.


